Euclid, Elements of Geometry
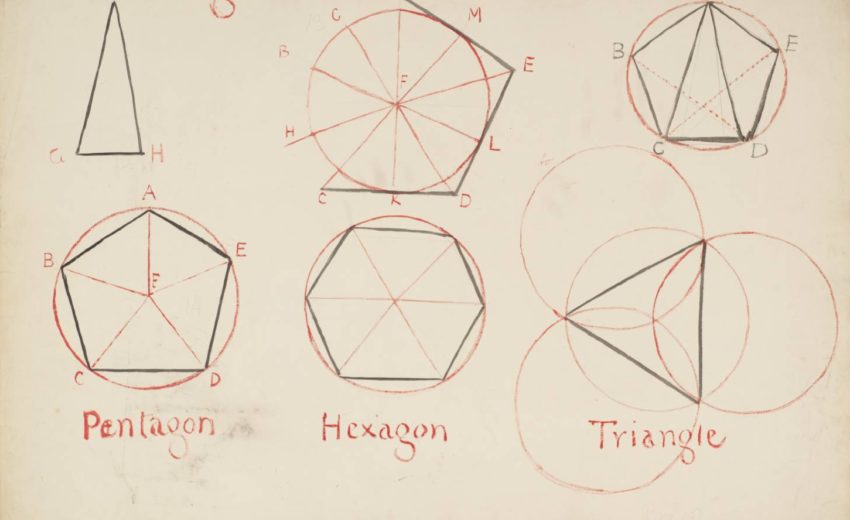
Euclid’s Elements is by far the most famous mathematical work of classical antiquity, and also has the distinction of being the world’s oldest continuously used mathematical textbook. Little is known about the author, beyondthe fact that he lived in Alexandria around 300 BCE. The main subjects of the work are geometry, proportion, andnumber theory.Most of the theorems appearing in the Elements were not discovered by Euclid himself, but were the work of earlier Greek mathematicians such as Pythagoras (and his school), Hippocrates of Chios, Theaetetus of Athens, and Eudoxus of Cnidos. However, Euclid is generally credited with arranging these theorems in a logical manner, so as to demonstrate (admittedly, not always with the rigour demanded by modern mathematics) that they necessarily follow from five simple axioms. Euclid is also credited with devising a number of particularly ingenious proofs of previously discovered theorems: e.g., Theorem 48 in Book 1. The geometrical constructions employed in the Elements are restricted to those which can be achieved using a straight-rule and a compass. Furthermore, empirical proofs by means of measurement are strictly forbidden:i.e., any comparison of two magnitudes is restricted to saying that the magnitudes are either equal, or that one is greater than the other.
Download
Euclid_Elements of Geometry.pdf
Euclid_Elements of Geometry.txt
Euclid_Elements of Geometry.html
Euclid_Elements of Geometry.jpg
Euclid_Elements of Geometry.zip



